What is Enterprise System (ERP)?
Earlier, in large organizations, different information systems were used to serve different business functions like sales, marketing, production, manufacturing, etc., separately.
An enterprise resource planning (ERP) system corporate with organizations to enhance business management and operations within a centralized database. Agencies incorporate ERP software to assimilate business processes, accumulate operational data, improve supply-chain effectiveness, stimulate data-driven strategies, and improve collaboration between compartments.
The business processes in each business function were disparate and not capable of sharing information with each other. It was difficult for the managers to assemble the data fragmented into separate systems in order to present an overall picture of the organization’s operations and take firm-wide decisions.
At the time a customer places an order, for example, the salesperson might not be able to tell him whether the desired items are in inventory or are to be produced.
To overcome such difficulties, in recent years, many organizations have opted to replace several distinct information systems with a single integrated system that can support business activities for different business functions. Such systems are called enterprise systems.
Enterprise System Overview
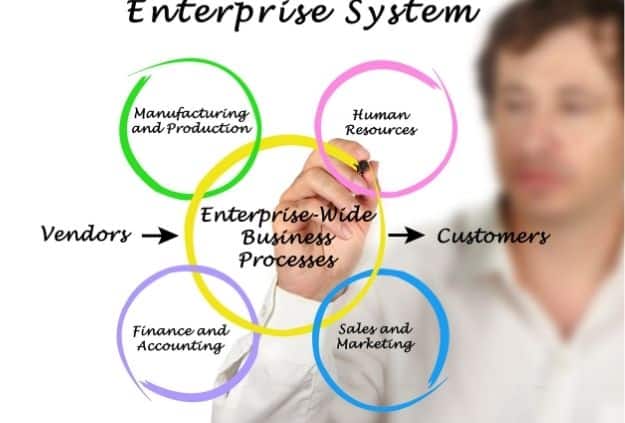
An enterprise system, also known as an enterprise resource planning (ERP) system, is a cross-functional information system that provides organization-wide coordination and integration of the key business processes and helps in planning the resources of an organization.
With the help of enterprise resource planning systems, information can flow seamlessly across the firm. Also, different business processes from sales, production, manufacturing, logistics, and human resources can be integrated into organization-wide business processes.
An ERP system is driven by the ERP software suite-a set of integrated software modules–and a common centralized database. The software modules support the basic business processes under different functional areas and the database stores data from and feed the data to various applications supporting the internal business activities.
Some examples of business processes supported by ERP software include accounts payable, general ledger, cash management, and forecasting, personnel administration, payroll, time management, inventory management, product pricing, billing, etc. Initially, ERP software was designed for automating a firm’s internal ‘back-office business processes, but now, it can also communicate with customers, suppliers, and other business partners.
For implementing ERP systems, organizations need to identify the business processes to be automated and then map those processes to the processes provided by ERP systems.
All this requires a great amount of effort. Moreover, organizations may find that the business processes of these systems are not able to support the way that the organization’s business processes work.
In such cases, the software may need to be customized to satisfy the requirements of the organizations. This may not only deteriorate the system’s performance but also need compromising the information and process integration.
Thus, to obtain the maximum benefit from enterprise resource planning software, the organizations should change their way of working according to the business processes of software instead of customizing the software.
Enterprise resource planning, supply chain management, and customer relationship management systems are examples of enterprise systems.
These systems are used as a central command hub to help automate the business and make reporting and decision-making easier.
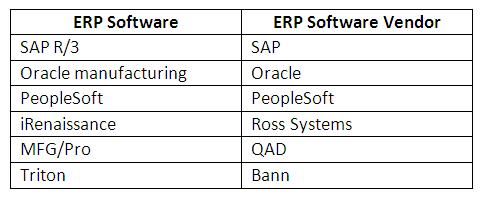
Nowadays, a variety of ERP software offered by different software vendors is available in the market.
Some major enterprise resource planning software along with their vendors are:
4 Benefits of Enterprise Resource Planning (ERP) Systems
- Communicate the critical firm-wide information on the business performance to managers all across the organization quickly, so as to enable them to make better decisions and at the right time.
- Reduce the cost involved in transaction processing, hardware, software, and IT support staff in a significant manner.
- Improve the quality and efficiency of customer service, production, and distribution by integrating the company’s internal business processes in sales, finance, production, custom logistics, etc.
- Help to create a more uniform organizational culture where everyone uses a similar type of processes and information to do business.
What Are ERP System Modules?
According to Oracle NetSuite “, Each ERP module is designed for specific business functions, providing the data, and supporting the processes that will help those employees do their jobs. Every module plugs into the ERP system, so the system provides a single source of accurate data, even as the business adds new modules. If the ERP system is the toolbox, the modules are the screwdriver, wrench, hammer, and other tools in the box that each has specific uses.
7 ERP Modules and Their Features
1. Accounting and Finance
The accounting and finance module keeps track of the organization’s finances, including allocations, planning, accounting, revenue control, and tax management.
2. Customer Relationship Management (CRM)
The CRM module makes it possible for businesses to manage client operations, such as marketing, sales, and customer service. Employees can monitor sales probabilities and customer channels. Users can also employ CRM in marketing operation management, including advertisements and lead generation campaigns.
3. Supply Chain
Similarly, the supply chain module monitors products from the point of manufacturing to distribution. Notable features include inventory, purchasing, shipping, tracking, refunds, claim processing, and supplier scheduling.
4. Inventory Management
The inventory management module makes it easy for businesses to track resources and supplies through purchase orders, automatic ordering, inventory control, and scanning.
5. Manufacturing
Manufacturers and other production-oriented amenities can execute the manufacturing module to control their shops, including features such as quality control, work orders, planning, manufacturing operations, bill of resources, engineering, and the overall production cycle.
6. Human Resources
The human resources module facilitates the hiring process – from recruitment all through succession. Agencies utilize the following HR module elements: payroll, time management, learning management, performance management, and applicant tracking.
7. Business Intelligence
A business intelligence module accumulates and inspects data from various sources and helps users define a better organization’s solution. Some notable features include scheduled reporting, visualization tools, customizable dashboards, and real-time data access.